About Us
We Are BizzBuzz Creations
BizzBuzz Creations is a full-service digital marketing agency dedicated to helping businesses thrive in the online world. Our team of experts specializes in creating customized strategies that drive results and deliver measurable ROI.
.png&w=1080&q=75)
Our Digital Marketing Services
How Our Digital Services Transform Your Marketing
We think that the first step to successful marketing is to really understand your business. Before we start any campaign, we spend time getting to know your business, your consumers, your rivals, and your long-term goals. This lets us come up with plans that are not only innovative, but also useful, relevant, and designed to have a meaningful effect on business.
We don't think that marketing should be the same for everyone. We make plans that are just right for your business because every firm has its own goals, problems, and customers. We plan everything, from the channels we use to the messages we send, around what will perform best for your brand and market.
It's not about guessing when it comes to successful digital marketing; it's about measuring, learning, and getting better. We keep track of every click, impression, and conversion to see what truly works. We use real data and insights to constantly enhance your campaigns so they perform better, waste less money, and give you a better return on your investment.
Your audience, not simply your brand, is what makes great content. We create content that speaks directly to your customers’ needs, questions, and motivations. Our content, which includes blogs, landing pages, advertising, and social media postings, is meant to teach, engage, and lead your audience to take action.

Why Brands Choose BizzBuzz Creations
All-in-One-Expertise
Leverage our all-in-one IT, digital marketing, and consulting services, strategically designed to fuel your business growth and success.
Tailored for You
We design customized strategies tailored to your specific business needs and objectives, ensuring optimal results and long-term success.
Proven Impact
Our proven track record deliver measurable results, enhancing visibility, driving traffic, and significantly increasing profits for business like yours.
Trusted Assistance
BizzBuzz Creations offers continuous support and optimization and keeping your digital footprint strong and impactful in the saturated market.
Our Recent Work
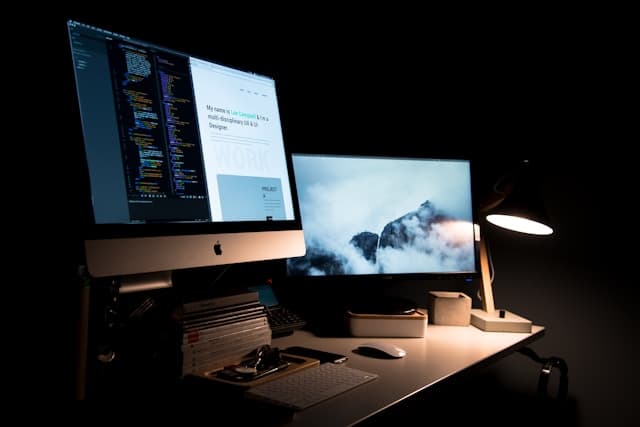

Website Development
Our website redesign initiatives are based on a clear plan, good user experience, and modern design. The results reveal that people are more interested, things happen faster, and more people buy on important pages.
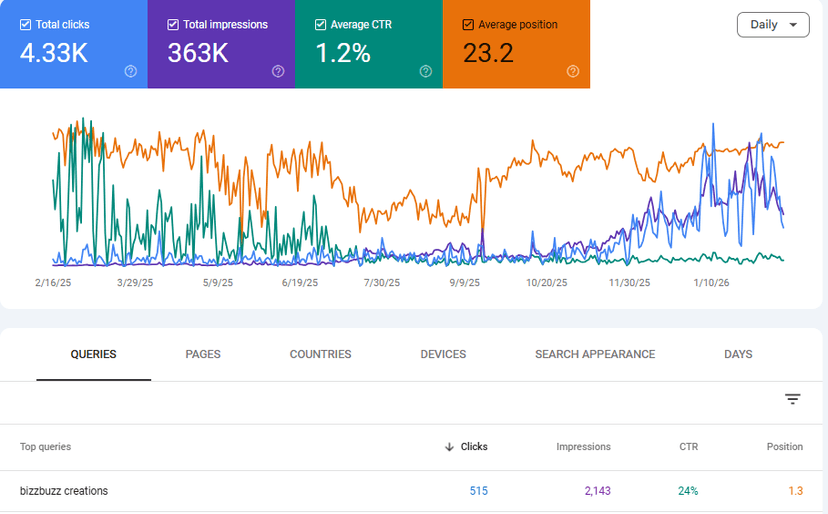
SEO Result Graphs
Our SEO campaigns are built on strong research, technical optimization, and quality content. The graphs of these results illustrate that search visibility, traffic growth, and keyword rankings have all steadily improved over time.

Social Media Creatives
We design social media visuals that align with your brand voice and marketing goals. Our creatives, from posts to advertising, are made to get people to interact with your brand, trust you, and make your online presence stronger.

Lead Generation Ad Results
Smart targeting, persuasive copy, and optimized landing pages are the main things our lead generation ads focus on. We assist companies get high-quality leads that are more likely to turn into genuine customers.
Our Clients
Customer Reviews
Sunayana Srivastava
Great Digital Marketing agency! Professional, creative & result oriented. Our campaigns have performed better than ever since partnering with BizzBuzz creations. Highly recommend their services.
Raunak Tripathi
Great experience with Bizzbuzz Creations. Professional, responsive, and delivered quality work on time. Highly recommended for growing your business.
Subhash Srivastava
Highly professional and competent team. Very cooperative and prompt their services. The city needs such a service providers. I would recommend this organisation highly to everyone.
Sarthak Mishra
Awesome experience with bizz buzz creations. Great for people and companies looking out for digital marketing agency.
Tariq Khan
Best digital marketing agency in prayagraj. They are very professional and cooperative. I am very happy with their services. I would recommend this organisation highly to everyone.
Rudra Pratap Singh
One of the best digital marketing service providers in Prayagraj. The team is highly trustworthy and delivers outstanding SEO results. Great experience overall!
50+
Projects Delivered
10000+
Leads Generated
4.9
Google Rating
3+
Years Experience
Our Latest Blogs
Explore, discover, and find inspiration through these exciting Blogs.

Mar 13, 2026 by Shreya
Voice Search Optimization in 2026: How to Rank for Conversational Queries
Voice Search Optimization in 2026: How to Rank for Conversational Queries Search behavior is evolving faster than ever. A few years ago, people mostly...
Read More
Mar 8, 2026 by Shreya
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): How to Rank in AI-Generated Results
Search is evolving rapidly. As discussed in our pillar guide on The Future of Digital Marketing in 2026: AI, SEO, Ads & Conversion Strategy, searc...
Read More
Mar 5, 2026 by Shreya
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): The New SEO Strategy for AI Search
Search is changing. People are no longer just clicking links — they are getting direct answers from Google. If you’re still doing traditional SEO only...
Read MoreHow It Works
IT Consulting & IT Services at Bizz Buzz Creations offer expert guidance and ongoing support to optimize your technology, improve security, reduce costs, and streamline operations—boosting productivity and keeping your business competitive.
At Bizz Buzz Creations, our IT services boost security with firewalls, encryption, system updates, and continuous monitoring, protecting your business from threats and ensuring data safety.
Increase lead generation by leveraging data-driven strategies, targeted campaigns, and personalized content to attract qualified prospects, nurture relationships, and convert them into loyal clients for sustained business growth.
Bizz Buzz Creations offers IT services including IT Management, Web Development, Cloud Computing, Tech Support, alongside Corporate Event Management, Financial Advisory, Business Consulting, Networking, Digital Marketing, and BPO Outsourcing solutions.
Track performance with real-time analytics, assess campaign effectiveness, and continuously optimize strategies to enhance ROI, improve outcomes, and ensure sustained growth by adapting to market trends and customer behavior.
Get Free Consultancy Now!
Ready to grow your business with trusted digital marketing services in UP? Contact Bizz Buzz Creations today and let’s build your success story together.

















